|
POWDER POST BEETLES
Picture courtesy : UC Riverside Entomology
In this section we will discuss four types of Powderpost beetles in four families: Lyctidae, Bostrichidae, Anobiidae, and Cerambycidae. Adults do little damage, it is the larvae that does the major part of the damage.They go through a complete metamorphosis: adults, eggs, larvae and pupae.
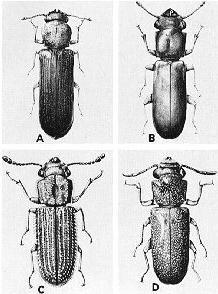
True Powderpost Beetles(Lyctidae):
The adults are very small, less than 1/4" in size. They are flattened and reddish-brown to black in color. Larvae are white, cream colored, c shaped with dark brown heads. Larvae create tunnels in the wood and become pupae. As adults they bore out through the wood, pushing a fine powdery dust out.The shape of their holes are round ,about 1/32-1/16 pinholes.
They attack hardwoods depositing their eggs. They can attack bamboo(technically a grass),but because of the large pores they will attack. Their diet is starch, sugar and protein in the sapwood of hardwoods Wood that is less than 6% moisture content is seldom attacked .The life cycle averages one year to complete .This wood-boring beetle is the most widespread in the United States. Many times infestations are built into structures from infested lumber .They can reinfest.
Lycid damage is characterized by:
- Presence of extremely fine, flour like powder falling from the surface holes.
- The frass left by other wood borers usually contains pellets, has a course texture and a tendency to stick together.
- When inspecting damage, be sure to distinguish old damage from active beetle infestations.
- Recently formed holes and frass(sawdust like) are light in color and clear in appearance....old holes and frass are dark in color.
False Powderpost Beetle(Bostrichidae)
They are larger than other families of powderpost beetles...so their exit holes are larger. These holes do not contain frass,but the galleries do. The frass is tightly packed, tends to stick together and is meal like( contains no pellets)
The adults are 1/8-to 1-inch long, cylindrical, and reddish brown to black. The adults bore into the wood in order to lay eggs, leaving a hole larger that 1/8 inch, usually in wood less than 10 years old.
The larvae are curved and wrinkled. Their diet is dependent on the starch in the wood, they are more common in softwood ,but can attack hardwoods. They require 6-30% moisture content in the wood, and complete the average life cycle in one year.
Most of the hardwoods attacked are not those commonly found used for interior floors,woodwork or trim. Most of this species does not reinfest wood after it is seasoned, so the damage is limited to that inflicted by one generation.
However the speed of the damage can be considerable.
Most of the time they do not reinfest wood after it has been seasoned. They are often found in oak, firewood and furniture.
Anobiid Powderpost Beetle (Anobiidae)- Furniture and Deathwatch Beetles
Tthe funiture beetle is found mostly in the eastern half of the United States and it infests structural timbors as well. The Death-watch beetel is found trhroughout the United States. It attacks building timbers in poorly ventilated areas where moisture tends to collect.
The name"Death watch" comes from the ticking sound that the adult makes inside infested wood that is audible during a still night. It is a mating call.
The insect is a common pest in the southeastern United States in crawl space timbers. Infestations can become so severe, that loss of structural strength to sills , joists, and subflooring occurs.
The Adults are 1/8-1/4 inch long. They are red to dark brown in color and their shaped is usually oval. The adults lay their eggs in the cracks and crevices of seasoned wood. As soona as they hatch, larvae burrow ito the wood where they live and tunnel for a year or more.
The larvae form tunnels in both softwoods and hardwoods They require 13-30% moisture content.
The larvae are slightly curved and wrinkled, with tiny hairs on the body.
Their holes are round,1/16-1/8 inches. They can digest cellulose from the wood. They are inclined to the softwoods ,for this reason they are common in crawl spaces and basements ,infesting the pine used as framing lumber.
The powder outside the holes (frass) is fine to coarse, many times with small pellets. The life cycle averages 1-3 years.
They commonly reinfest crawl space areas that are poorly ventilated and humidity is absorbed in the wood.
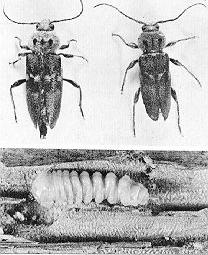
Old House Borer(from the family Cerambycidae)
Picture courtesy : UC Riverside Entomology
The Old House Borer is one of the most common from this family, with it's larvae hollowing out galleries in seasoned softwood(pine). It is found in older buildings, but is more frequent in newer buildings,(in houses less than 10 years old).The adults are brownish-black to black, slightly flattened and about 3/4-1 inch long.
The average life cycle is usually one to three years, but can take up to twelve years if nutritional and environmental conditions are unfavorable. Because of the long life cycle, reinfesting the wood it may take years before you see any structural damage .
The exit holes are about 1/4-3/8-inch in diameter, but damage may have occurred for several years before spotting such holes. They are able to digest cellulose.
When wood has been infested with fungi, the larval development is faster. Their powder (frass) in the tunnels are like sawdust ,tightly packed.
INSPECTION FOR WOOD BORING BEETLES:
- Inspect periodically all exposed wood surfaces and probe them for evidence of internal damage.
- Evidence of attack is more common in attics, crawl spaces , unfinished basements and storage areas.
- To be certain that the infestation is active(not old damage or old frass), there should be fresh frass the color of newly sawed wood, or live larvae or adults in the wood.
CONTROL AND RECOMMENDATIONS:
- The first thing to do is reduce the moisture content, to a proper ventilation to less than 20%.Moisture meters can be used to determine the moisture level in the wood. Central heat,vapor barriers and good ventilation can help control moisture.
- If practical..remove infested wood. If not,use residaul borate insecticides.
- Recommended products are two borate insecticides:
TIMBOR is a powder that mixes with water. One lb.is mixed with one gallon of water and sprayed to the surface area of in infestation. When sprayed it penetrates the entire wood, where it will remain for several years .An alternative to Timbor is:
BORACARE. Boracare is a liquid borate that penetrates faster initially than the Timbor for first few hours but is equal after that..Timbor is considerabley cheaper per gallon use.
|